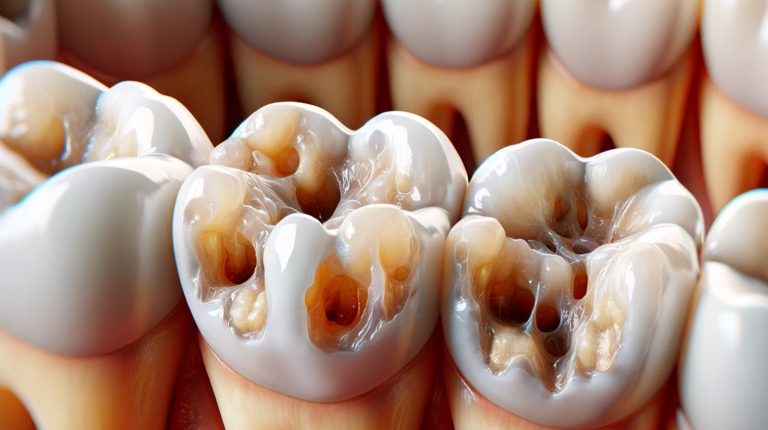
Dental caries
What is dental caries?
Dental caries or tooth decay is often called the “top dental adversary for humanity.” It afflicts a staggering 93% of the global population. Evidence of this ailment has been discovered in individuals who lived as far back as 5-6 thousand years ago. Today, dental caries in adults is responsible for nearly 90% of tooth loss cases. Moreover, it doesn’t just result in the familiar “cavities.” As the pathological process extends to adjacent areas, it triggers periodontitis and, eventually, the total deterioration of the tooth, necessitating the irremovable extraction of its remnants and roots.
What are the causes of tooth decay?
The cause of this disease is the large number of microorganisms in the human oral cavity. The destruction of first enamel and then dentin (the hard substance of the tooth) with further damage to the pulp chamber occurs under the influence of acids that these bacteria release in their life activity.
Their reproduction is especially intensive in plaque thickness, so periodic professional tooth hygiene is one of the most effective methods of preventing dental caries.
Types of caries
This disease can be classified according to the localization of the pathological process:
- Cervical caries. In this case, the defect occurs at the border of the tooth and gum.
- Interproximal caries. In this case, the sides of two neighboring tooth crowns are affected at once. Decay between teeth occurs mainly because these areas are difficult to clean with a toothbrush.
- Fissure caries. A fairly common variant in which the defect appears in the folds formed by the hard tissue on the chewing surfaces of the tooth.
- Root caries. An infrequent lesion but the most difficult to diagnose because the defect is hidden under the gum.
In addition, this disease has several stages of development. The following stages of tooth decay are distinguished:
- Initial, when the lesion appears as a dark or light spot on the tooth enamel;
- superficial caries, in which the pathological process develops only in the enamel layer;
- medium tooth decay, when the lesion has already spread to the upper layers of dentin;
- deep tooth decay with the spread of the defect into the deep layers of dentin and into the pulp chamber.
Caries diagnosis
The diagnosis is made by a dentist based on the characteristic symptoms of tooth decay and examination of external damage to the tooth. The stage of pathology is clarified by radiography or computer tomography.
Signs of tooth decay
- Dental sensitivity
- A range of mild to intense discomfort while consuming hot, cold, or sweet items.
- Visible cavities
- Stains in brown, black, or white shades on any tooth surface
- Pain on biting or chewing
How do you cure tooth decay?
Treatment of caries depends on the stage of its development. Thus, in caries at the stage of stain, it is sufficient to remineralize the enamel using special solutions and pastes. If the destruction of hard tissues has begun, it will require mechanical cavity cleaning and cavity filling.
Particular attention should be paid to situations when the carious lesion has reached the inner cavity of the tooth, where the nerve bundle is located – the pulp. In this case, its inflammation develops – pulpitis, for the treatment of which it is necessary to fill dental canals. These canals connect the pulp cavity with the jawbone and can become a pathway for bacteria. This is how periodontitis occurs, the main cause of complete tooth loss.
The method of treating a caries complication is the most complex and consists of several steps:
- Pulpectomy. Root canals are pre-cleaned using automatic or manual instruments. It is essential to carefully remove all soft tissues so that they do not become a focus of inflammation in the future.
- Root canal irrigation. Then, all bacterial microflora in the dental canal should be destroyed. For this purpose, dentists use special dental antiseptics.
- Wall shaping. The doctor tries to straighten the canal as much as possible and smooth out any protrusions on its walls. This will ensure the reliability and quality of the filling.
- Root canal filling. The canal is completely filled with a sealed material. Particular attention is paid to tight closure of the root tip,apex. In the end, radiography is performed to control the quality of filling.
- Tooth Restoration. This procedure restores the anatomical shape of the tooth, restoring chewing function and natural appearance.
Caries prevention
According to the World Health Organization statistics, competent preventive measures can reduce the risk of tooth decay in children by 80% and almost completely eliminate the loss of teeth due to this cause in adulthood.
Why is this necessary?
- Prevention instead of treatment. Even in its early stages, tooth decay involves some tooth tissue damage. While a dentist can repair the tooth and create a filling to replace the missing portion, the filling acts as a less effective substitute for the lost tooth tissue. Prevention, on the other hand, prevents the disease from progressing, maintaining the tooth’s natural structure and eliminating the necessity for artificial replacements.
- Prevention is easier than treatment. Therapy of carious lesions, especially in cases of their large-scale spread, is time-consuming. And no one can guarantee that the disease will not reappear on another tooth. Performing regular prophylaxis is much faster. This procedure lasts only about an hour, does not require complex dental manipulations, and should be carried out on average only twice a year.
- Finally, prevention is cheaper than treatment. Financially, preventing tooth decay is also much cheaper than an entire course of treatment. Therefore, by carefully monitoring the condition of the oral cavity and preventing the development of the disease, you not only take care of your health but also save money!
On Doctor.Global there are 262 clinics worldwide where any type of caries can be treated (https://doctor.global/results/diseases/dental-caries). The cost of dental caries treatment depends to a large extent on the stage of the disease. For example, the cost of treatment of medium caries in a Latvian clinic is 108$, while treatment of one canal in case of complicated caries starts from 323$ (https://doctor.global/clinic/dental-art#prices).
Is it possible to take care of your dental health on your own?
Yes, of course. There are some rules that, if followed daily, will significantly reduce the risk of developing carious lesions:
- Brushing twice a day allows you to remove soft plaque, in which bacteria breed. To reliably get rid of it, you need to brush your teeth in the morning and evening with a brush that has medium bristles. The procedure should last at least 3-4 minutes. Alternating between fluoride toothpaste for one week and non-fluoride toothpaste for three to four weeks is a suitable approach. This periodicity is based on the reality that enamel can only absorb a certain amount of fluoride. A week of using fluoride paste will provide the enamel with a sufficient amount of this element, and then fluoride will simply be excreted from the body. But after a month, its concentration will decrease, and its inflow will be needed again.
- Floss at least once a day to supplement the procedure, as brushing cannot fully clean the spaces between your teeth.
- Regular cleaning after meals. Food residues should be removed with a regular rinse. It should be done after each meal.
- Watch out for sweets! Bacteria that cause tooth decay multiply much more intensively in an environment rich in sugars and fats. Therefore, instead of another cake, it is better to eat an apple or a carrot. On the one hand, you will deprive the bacteria of additional nutrition; on the other hand, the hard consistency of such foods cleans the teeth and removes soft plaque.
The preventive measures described above can be carried out on your own. However, you can only do this with the periodic assistance of a dental professional.