Ulnar fracture
What’s that?
Fracture of the ulna is characterized by damage to its integral structure; in some cases, the adjacent joint may also be affected.
About the disease
Injuries of this localization occur due to a fall on the elbow or a mechanical impact of the bones during a car collision with an obstacle, for a fracture of the ulnar bone is characterized by sharp pain, which increases when trying to move the arm—visually determined swelling and lividity. The function of the hand is impaired.
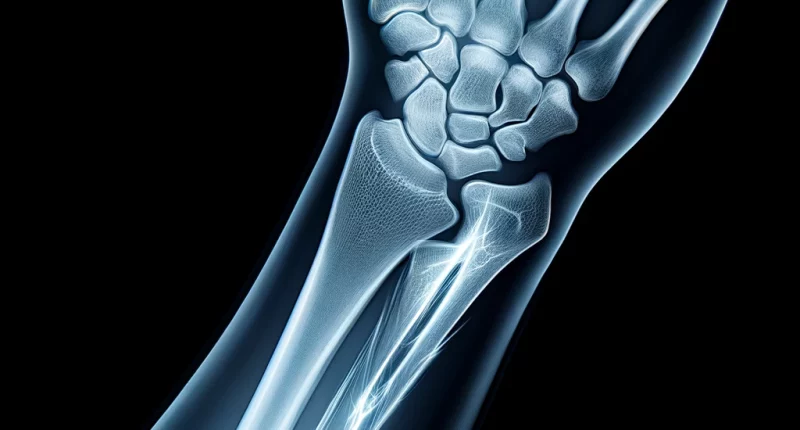
The diagnosis is made based on X-ray scan data. The image clearly visualizes the line of injury and the topographic relationship of the bone fragments. A CT or MRI scan may be required to detail the injuryin fractures involving the joint.
Considering the injury’s severity, the doctor chooses conservative or surgical treatment tactics. Surgery is usually performed for complicated fractures.
Types of ulna fracture
According to the classification, the following types of fracture of the ulna are distinguished:
- Alterations with and without displacement of bone fragments.
- Self-inflicted injuries in which the integrity of one bone is compromised, and combined injuries in which, in addition to the fracture, there is also dislocation of the forearm bones in the elbow or wrist joint.
- Traumatic injury to the body of the ulna (diaphyseal), proximal or distal end of the ulnar bone (injuries in the region of the ulnar head, styloid process).
- Intra-articular, extra-articular and periarticular fractures.
Symptoms of a fracture of the ulna of the arm
Symptoms of a fracture of the ulna of the arm may include the following:
- intense pain in the injured part of the forearm;
- change in limb length or shape (this is a variable sign that may be positive for a complete fracture);
- swelling of the forearm;
- a severe limitation in the ability to move the upper extremity;
- impaired flexion and extension of the elbow or wrist joint;
- limitation of internal and external rotation of the hand;
- unnatural mobility of the forearm (in case of simultaneous fracture of the ulna and radius);
- spring effect (determined in combined radius dislocation).
Reasons
An ulna fracture results from a mechanical impact, with the applied force exceeding the strength of the bone tissue. Such injuries can occur due to a fall or a direct blow to the forearm.
Diagnosis and joint involvement
Diagnosis is based on the data of objective examination and palpation of the affected area. Signs that indicate an elbow fracture may be:
- tissue swelling;
- increased soreness on palpation;
- spilled lividity of the skin;
- curved forearm shape;
- the inability to make a fist;
- bone crepitation.
In some cases, a fracture of the ulna may be accompanied by the development of compression syndrome due to increasing subfascial edema. Against this background, intrathecal pressure increases, and nerve trunks are compressed. This condition is manifested by progressive pain, which increases with finger traction.
Treatment of a fracture of the ulna
Treatment of ulna fractures may involve both conservative and operative management tactics. Fractures should be treated promptly to prevent immediate and delayed complications (damage to the radial nerve, major feeding vessels, etc.).
Conservative treatment
Uncomplicated fractures are usually treated conservatively under adequate anesthesia. The main stages of therapeutic care are:
- In displaced fractures, manual repositioning is performed first;
- After closed repositioning, an X-ray scan is performed to determine the correct position of the fragments;
- Application of a circular immobilizing dressing made of plaster or polymer.
In the case of non-displaced fractures, an immobilizing dressing is applied immediately. The severity of the injury determines the period of plaster/polymer wear, which can be 4-6 weeks. During this time, a bone callus is formed to hold the fractures together.
All patients with an ulna fracture are given anesthesia for the first week. Usually, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used for this purpose. Calcium and vitamin D preparations are prescribed to improve bone regeneration.
Surgical treatment
Surgery for ulna fracture is indicated in the following cases:
- bone injuries with displacement, manual repositioning of which was unsuccessful;
- inability to provide reliable immobilization by conservative method (e.g., in case of soft tissue interposition between bone fragments);
- multislip fractures.
The operation consists of matching the bone fragments under visual control. To keep them in relation to each other, fixation with titanium plates/pins and screws is performed.
In fractures with skin damage, the first step is the surgical treatment of the wound – necrotized tissue, foreign objects, blood clots, and bone fragments are removed. The wound is abundantly washed with an antiseptic solution. An external fixation device is used to ensure the immobility of bone fragments. It allows you to monitor the healing of the wound and conduct regular treatments.
All these treatment options are available in more than 800 hospitals worldwide (https://doctor.global/results/diseases/ulnar-fracture). For example, Forearm fracture surgery is performed in 40 clinics across Germany for an approximate price of $7.3 K (https://doctor.global/results/europe/germany/all-cities/all-specializations/procedures/forearm-fracture-surgery).
Prevention
The prevention of ulna injuries is aimed at preventing injuries. For this purpose, it is recommended to follow the road traffic regulations, be cautious when performing household tasks, and use protective equipment when working at heights. In the winter season, it is essential to be careful on icy conditions of roads.
Rehabilitation after an ulna fracture
Rehabilitation after an ulna fracture begins at the immobilization stage. It is recommended to move the fingers regularly to prevent muscle atrophy and reduce the risk of contracture development. After the cast/polymer is removed, the active stage of recovery begins, which includes the following components:
- development of the joint with special exercises;
- physiotherapy treatments;
- therapeutic and revitalizing massage.
At the final stage of rehabilitation, it is recommended to massage the injured forearm yourself and gradually increase the load on the limb. It is useful to perform taping.