Retrocalcaneal bursitis
What’s that?
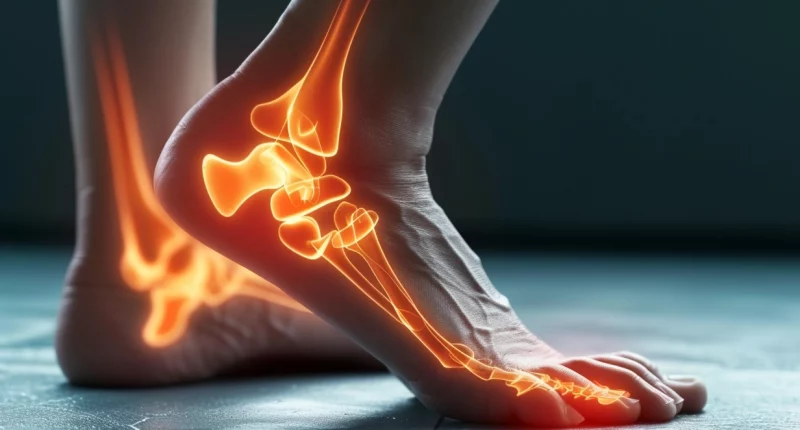
Retrocalcaneal bursitis, or foot bursitis, is an inflammatory lesion of one or more synovial sacs involved in foot joint formation.
About the disease
In most cases, the pouch located in the area of the first articulation of the phalangeal and metatarsal bones, the bursa of the heel tendon, or the pouch of the heel area itself becomes inflamed. The pathology is manifested by classic signs of inflammation – pain, redness, swelling, elevation of local body temperature, and impaired functional status of the foot.
Bursitis most often has a primary chronic course. Acute forms are usually due to infection of the articular joints. With untimely treatment of acute bursitis, the pathology is transformed into a sluggish inflammation.
Bursitis is most common in middle-aged and older people. The exception to this rule is athletes, in whom the most common form of the disease is Achilles bursitis, which develops at a young age.
Diagnosis of inflammatory lesions of the articular joints of the foot is based on a thorough evaluation of clinical symptoms and objective examination data. The final diagnosis is based on imaging methods, particularly radiography and ultrasound scanning. In complex clinical cases, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging is used.
Treatment of bursitis is usually carried out conservatively. An integrated approach allows you to achieve the desired result. Surgical intervention is performed when purulent inflammation of the bursa develops.
Types
According to localization, the following types of foot bursitis are distinguished:
- Achilles bursitis – the joint pouch, which is located in the area of the Achilles tendon attachment, becomes inflamed;
- Subcalcaneal bursitis – the pouch located in the area of the lower part of the heel becomes inflamed;
- Bursitis of the first toe is caused by inflammation of the bursa located in the junction of the first phalangeal and the metatarsal bones.
Symptoms of foot bursitis
Symptoms of foot bursitis may include the following:
- painful sensations in the area of the inflamed bag;
- redness and swelling of the skin over the affected pouch;
- localized increase in skin temperature.
Painful sensations in the initial stages of the disease appear only after prolonged walking or prolonged wearing of non-ergonomic shoes. Later, pain may occur even at rest, including during night sleep, causing insomnia. In carpal bursitis, the pain becomes particularly intense if the patient tries to lift himself on his toes.
The localization of the inflamed pouch determines clinical signs. Visual inspection often reveals symptoms of bursa inflammation and predisposing factors in the form of foot deformity. Thus, with bursitis of the first metatarsophalangeal joint, an “ossicle” on the inner surface of the foot is determined, as well as corns in places where the skin experiences excessive mechanical pressure. In severe cases, the first toe of the foot overlaps the second toe, indicating a severe degree of deformity.
Reasons
Inflammation of one or more synovial joints of the foot is most often caused by repetitive traumatization of the joints. Predisposing factors increase the likelihood of developing the disease. The following conditions can play a role:
- Presence of foot deformities – most commonly Hallux, heel spurs, flat feet, clubfoot;
- Associated acquired diseases of the musculoskeletal system (plantar fasciitis);
- Repeated traumatization of the foot, including those associated with physical activities (long jumping, athletics, etc.);
- Excessive body weight, which increases the load on the joints and periarticular tissues;
- Biological aging of the body, when dystrophic processes are triggered in many tissues (in women, bursitis can often be associated with the onset of menopause);
- Thinning of subcutaneous fatty tissue in the area where synovial sacs are located under the skin;
- Deforming osteoarthritis of medium and small joints of the lower limb;
- Wearing compression shoes, which has an unfavorable mechanical effect on the musculoskeletal apparatus of the foot;
- Spinal column pathology, which increases the load on the feet;
- Metabolic and autoimmune disorders in the body.
Diagnosis
Visualizing diagnosis of foot bursitis involves several examinations from this list:
- Radiography of the foot – allows to identify bony deformities that indicate a possible cause of inflammation of the synovial pouch;
- Ultrasound scanning of the joints of the foot – helps to determine the involvement of soft tissue formations in the pathological process;
- Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging- are used in complex clinical cases where it is necessary to detail the structure of bone structures, cartilage plates, joint capsules, and periarticular tissues.
Treatment of bursitis of the foot
Complex conservative therapy is usually sufficient for treating inflamed articular joints of the foot. Surgical intervention is performed for two indications – the development of purulent inflammation and/or correction of concomitant pathology of the musculoskeletal system.
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment of foot bursitis involves limiting the load, wearing unloading orthopedic shoes, and carrying out a physiotherapy course.
Urgent care for bursitis is to control the pain syndrome. For this purpose, local and systemic forms of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used. If pain is not reduced, a short course of corticosteroids is indicated.
Surgical treatment
In purulent bursitis of the foot, the affected bursa is opened, destructive tissues and purulent contents are evacuated, the cavity is washed, and a drain is installed. It provides adequate outflow of wound secretion and promotes its cleansing. After the acute process subsides, the drainage is removed.
If the foot has deformities that create conditions for inflammation of the synovial joints, appropriate reconstructive-plastic surgery is recommended to prevent the recurrence of bursitis.
All these treatment options are available in more than 800 hospitals worldwide (https://doctor.global/results/diseases/retrocalcaneal-bursitis). For example, heel bursectomy can be performed in 45 clinics across Germany for an approximate price of $7.5 K (https://doctor.global/results/europe/germany/all-cities/all-specializations/procedures/heel-bursectomy).
Prevention
Prevention of inflammatory lesions of the foot joints of involves following simple rules:
- wearing comfortable shoes that do not squeeze the foot, the optimal heel height is 3-4 cm;
- use of orthopedic insoles to cushion the impact while walking;
- timely correction of foot deformities if they pose a danger to healthy segments of the limb.
Rehabilitation
After opening the purulent focus of the synovial bag, it is essential to provide functional rest of the foot to create conditions for complete wound healing and tissue repair. For the first few days, walking with the use of crutches or an orthopedic cane is recommended. After the acute process subsides, physiotherapy and therapeutic exercises to improve the foot biomechanics are helpful.