Scoliosis
What is it?
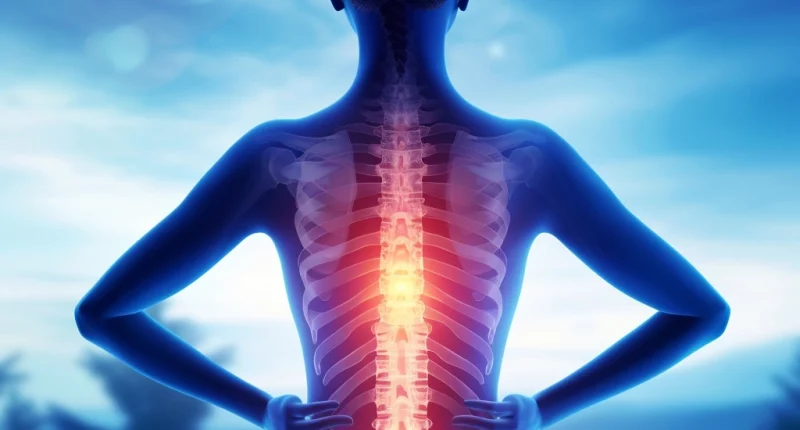
Scoliosis is a persistent skeletal deformity manifested by lateral misalignment of the spine. A change in the position of the vertebrae in the anteroposterior direction usually accompanies lateral curvature of the spine. Gradually, the disease is complicated by deformation of the thorax and pelvic bones and damage to internal organs. In most cases, pathology begins to develop at the age of 5 to 15 years, when there is an active formation of the musculoskeletal system. The already arisen curvature gradually worsens. Scoliosis treatment should be comprehensive: doctors prescribe special exercises, therapeutic procedures, and surgical interventions.
Scoliosis can be a congenital or acquired condition. It is the most common type of skeletal deformation. In the early stages of the formation of the disease, the curvature can be detected only by radiography, but later, scoliosis manifests itself with external signs. Respiratory disorders and chest and back pain can accompany significant curvature of the spine. In old age, the disease can be significantly complicated. Orthopedists recommend starting treatment of this pathology as early as possible.
Symptoms of scoliosis
The first stages of scoliosis have no apparent signs. As the degree of deformation of the spine increases, external signs of the disease appear, associated with the position of the upper limb girdle and the shape of the back and waist. Symptoms of dysfunction of internal organs usually appear in the late stages of scoliosis.
Possible signs and symptoms:
- The shoulders and shoulder blades are at different levels;
- Unsymmetrical waist shape;
- Noticeable curvature of the spine during back bending;
- Different lengths of upper extremities when extending arms;
- A change in the shape of the neck;
- The anterior ribs are strongly protruding (especially in the supine position);
- A pronounced pelvic deformity;
- Rib recession;
- Chest, back, or neck pain.
Symptoms of scoliosis dependson the degree and area of spinal deformity. Curvature can occur in the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar regions. To the late signs of the disease, doctors include rib hump and stretching of skeletal muscles in the area of bone deformation.
Causes of scoliosis
In most cases, the cause of the disease is unknown. The curvature of the spine is believed to result from a combination of genetic and external factors. It may be an inherited trait that begins to manifest itself during puberty, or it may be the result of trauma.
Muscle and nervous system abnormalities can also cause curvature of the spine. In about 65% of cases, orthopedists do not identify the cause of bone deformity (idiopathic scoliosis). Women are more prone to this disease.
Possible causes:
- Genetic mutations. Alteration of DNA sites responsible for the formation of the musculoskeletal system can cause scoliosis. For example, mutation of the CHD7 gene is directly related to the formation of this disease;
- Congenital bone malformations. Usually, fundamental changes occur in the first six weeks of a new body’s development;
- Muscular system abnormalities. Skeletal muscles support the correct development of the spine, so any diseases of this system can cause bone deformity;
- Congenital condition due to diaphragmatic hernia, connective tissue development disorder, Loeys-Dietz syndrome, and other pathologies;
- Acquired viral disease (polio).
Many forms of scoliosis are hereditary, so it is essential to evaluate a child’s spine if there is an unfavorable family history.
Scoliosis diagnosis
If symptoms of scoliosis are detected, it is necessary to make an appointment with an orthopedist. The doctor performs a general examination, which includes assessing the degree of physiologic curvature of the spine and examining the joints. The orthopedist also examines the chest and muscles to detect additional signs of the disease. The examination occurs in the patient’s sitting, lying, and standing positions. The data obtained during the examination are sufficient to detect scoliosis, but the orthopedist prescribes instrumental studies to clarify the degree of bone deformation and search for complications.
Additional examinations
- Radiography of the spine. The orthopedist prescribes this diagnostic manipulation to assess the spine’s condition. The patient is asked to assume a standing or lying position during the examination. If necessary, a slight stretching of the spine is performed. With the help of a special apparatus, the doctor receives images of the spine in two projections, which show all the features of the bones and joints. According to the images, the orthopedist assesses the degree of scoliosis. To monitor treatment and assess the rate of progression of the disease, the orthopedist conducts spinal radiography 1-2 times a year;
- Other methods of imaging the spine. In children, the doctor needs more frequent visual examination of the bones, considering the development of the musculoskeletal system. The orthopedist prescribes harmless manipulations to exclude excessive radiation load on the body. If necessary, the orthopedist conducts a three-dimensional ultrasound examination of the spine, which involves obtaining an image of the bones using high-frequency sound waves. Ultrasound of the spine can be performed without restrictions;
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine is the most accurate imaging examination to find the cause of scoliosis. This method involves nuclear magnetic resonance so the patient’s body does not receive radiation exposure. Before the examination, the doctor asks the patient to remove all metal objects. MRI results are images of tissues in different planes and slices. The tomography data are used to search for complications of scoliosis on the part of internal organs.
Conservative treatment of scoliosis
If the angle of curvature of the spine does not exceed 40 degrees, conservative scoliosis treatment is carried out to prevent further disease progression. For the selection of therapy, a consultation with an orthopedist and a doctor-vertebrologist is carried out. With a significant deformation, treatment is carried out in hospital conditions. In childhood, the main task is the timely normalization of the spine’s shape.
Correction methods were carried out.
- Orthotic devices eliminate the root cause of scoliosis and adequately distribute the load in different parts of the spine. Depending on the diagnostic data, the orthopedist prescribes special shoes or a corset for the patient. The use of corsets shows excellent results during the period of bone growth, but adult patients are prescribed a different treatment;
- Therapeutic exercises aim to normalize the spine’s shape and ease the load on the joints. Exercises are suitable for patients of any age. The orthopedist shows the patient how to perform specific exercises correctly. Some exercises are recommended to be performed every day at home. Gymnastics can be combined with wearing a corset and orthopedic shoes.
Orthopedists perform safe methods of scoliosis correction, focusing on the patient’s gender, age, and individual history. If necessary, consultation with a cardiologist, pulmonologist, or other physician is prescribed to treat complications of the disease.
Surgical treatment of scoliosis
The main indication for surgical intervention is a significant curvature of the spine (more than 45 degrees). In this case, the effectiveness of conservative therapy and the general state of health of the patient are preliminarily evaluated. Surgical scoliosis treatment involves using unique structures that fix the spine in the correct position.
In such cases, stabilization surgery is performed to immobilize the affected spine and fix the bones in a particular position. The doctor uses titanium plates, screws, and other metal structures to reshape the spine. To gain access to the bones, the surgeon first makes a soft tissue incision in the area of the tenth intercostal space. During the operation, the doctor eliminates compression of the spinal cord and thoracic organs. Experienced surgeons perform the safest intervention and prescribe rehabilitation for the patient to adapt.
All these treatment options are available in more than 770 hospitals worldwide (https://doctor.global/results/diseases/scoliosis). For example, Instrumented spine stabilization can be performed in 31 clinics across Turkey for an approximate price of $13.6 K (https://doctor.global/results/asia/turkey/all-cities/all-specializations/procedures/instrumented-spine-stabilization).
Scoliosis prevention
Even with a predisposition to scoliosis, it is possible to carry out preventive measures to normalize the spine’s shape. Prevention is recommended to be carried out in childhood.
Physician’s Guidelines:
- Performing orthopedic exercises for ages four and up under the supervision of a physician;
- Timely radiography in the presence of predisposition to the disease;
- Careful monitoring of the child’s posture.