Radiation therapy in clinics: Revolutionizing cancer treatment
Discover the incredible potential of advanced cancer treatment techniques in medicine. Explore the latest breakthroughs, information, and benefits revolutionizing patient outcomes.
What is radiation therapy?
Radiation therapy uses high-energy ionizing radiation to treat cancer. These radiations can be X-rays, Gamma rays, and particle radiations (protons, neutrons, etc.). These ionizing radiations result in the formation of ions inside cells. These ions cause irreversible damage to DNA causing the death of cancerous cells and shrinkage of tumors. There are three main modalities for cancer treatment. These include surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy medications. Radiotherapy can be used alone or in combination with the other two modalities. Combination with other modalities depends upon the type and stage of cancer.
Can radiotherapy cause cancer?
There is a small risk of cancer in radiotherapy patients secondary to radiation. But the chances are very low. The benefit outweighs the risk.
Types of radiotherapy
There are two main types of radiotherapy. These are external beam radiotherapy and internal radiotherapy:
- External beam radiotherapy
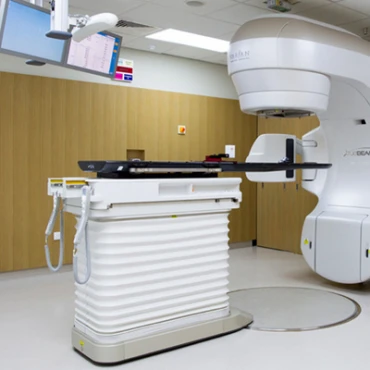
External beam radiotherapy is also called teletherapy. The radiation beam from a machine at a distance outside the body is directed toward the tumor. The different types of external radiotherapy are:- Conformal radiotherapy
In this type, a 3D image is constructed using CT, MRI, and PET scans. It helps to shape the radiation beam according to the tumor's shape. As the radiation is focused on only the cancerous cells the healthy tissue is spared. - Intensity-modulated radiotherapy
It is a type of conformal radiotherapy. In this type, each beam of radiation is subdivided and each beamlet intensity can be manipulated. So, it enables different dosage distribution across the tumor. It is very helpful in head and neck tumors. - Image-guided radiotherapy
In this type, frequent imaging of target tissue is done before each session to adjust treatment. The position of the patient in which imaging is done should be the same every time for easy comparison. The first few scans also aid in the diagnosis of cancer. Sometimes metal markers are placed near tumors which helps in the marking of the treatment area to make it more accurate. As radiation is targeted very accurately there is less chance of radiation to healthy tissue. - Stereotactic radiotherapy
In this type, different beams of radiation are focused on tumor cells from different angles. When used for the lungs, neck, spine, liver, and lymph nodes, it is called stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT). It is also used for brain tumors such as pituitary adenomas, acoustic neuromas, etc. A gamma knife device or a linear accelerator (linac) is used to deliver radiations for this purpose - Proton beam therapy
In proton beam radiotherapy, either high or low energy is targeted toward the tumor. It is only used in a few tumors so most people don’t need proton beam radiotherapy. Protons only travel a certain distance. So, only the cancerous tissues receive maximum radiation, and the healthy tissue is spared. It is used in cancer of the brain, spinal cord, melanoma, prostate, and cancers of the head and neck area.
- Conformal radiotherapy
- Internal radiotherapy
In this form of radiotherapy, radiation is given to tumor cells from inside the body. In this type, the radiation source is within the body at the destination near the cancerous cells. It helps in sparing healthy tissues and delivering high-dose radiation to the tumor. There are two main types of internal radiotherapy:
Radioactive liquid
The radioactive substance can be given to the patient in the form of a capsule, drink, or injection. After absorption in the body, it collects in the cancerous part of the body. It prevents harmful effects on normal tissues. Examples are:- Radioactive iodine (I-131) for thyroid cancer
- Radioactive strontium (strontium89) is similar to calcium. It is absorbed by bones and used for cancers that have spread to bones
- Radium223 is used in patients with prostate cancer spread to the bone
- Radioactive phosphorus (P-32) used in polycythemia Vera
Brachytherapy
A type of radiotherapy, in which a radioactive substance is placed into or near cancerous cells. The radioactive substance can be in the form of seeds, wire, discs, or tubes. They deliver radiation to the target tissue and healthy tissue is less affected.
There are two main types of Brachytherapy:
1. High-dose-rate brachytherapy
A radioactive source is inserted through applicators under general anesthesia. The radioactive source travels to the desired location. It is kept there for 10-15 minutes and then removed from the body. You might require a single dose or multiple doses over several days. When the radioactive source is removed you are no longer radioactive.
2. Low-dose-rate brachytherapy
The radioactive implant is placed inside or near cancer cells for days to weeks. This implant delivers a low dose of radiation continuously over a long period of time. Till the implant is inside the patient’s body, the patient is radioactive. The patient has to stay inside the hospital and should not come in contact with children and pregnant females. When the implant is removed patient can go home.
A team of expert doctors uses this mode in oncology centers abroad for the tumors of the female reproductive tract, prostate, and eye tumors. For bowel cancer, that has liver metastasis, selective internal radiation therapy is used. In the selective type, radioactive substances are placed in blood vessels carrying blood to the liver.
When is radiotherapy used?
Radiation therapy is given to more than half of cancer patients. When and which type of radiotherapy is to be given, depends on the type and stage of cancer.
Radiotherapy can be given in the following ways:
- Curing cancer
Some cancers are radiosensitive so they respond well to radiotherapy. It can either be used alone or combined with other treatment modalities. It is called neo-adjuvant therapy if radiation is given before surgery to shrink the tumor. If it is given after surgery to prevent a recurrence, it is called adjuvant therapy. - Chemo-radiation
It can also be used along with anti-cancer drugs. Some drugs increase the sensitivity of the cancerous cells for radiation therapy - Palliative
In advanced stages of cancer, radiotherapy can be used in palliative care. The main purpose is to control bone pain and relieve pressure such as in the brain and spinal cord. It is also used to relieve obstruction of blood vessels such as venae cavae to relieve bleeding. - Total body irradiation
This is a type of radiation therapy in which stem cells are destroyed by whole-body irradiation. This is used for stem cell transplants in leukemia patients. Radiation is combined with chemotherapy.
Benefits of radiotherapy
There are three main modalities for the treatment of cancer at the clinical level. Choosing the suitable treatment depends upon the type, stage, location, and radio sensitivity of cancer. There are a number of benefits for which radiation therapy is recommended:
- Radiation therapy in clinics is among the outpatient procedures. It means that you don’t have to get admitted to a health care center. However, you need to get an appointment.
- You can perform your daily activities along with radiotherapy sessions.
- If it is used before surgery it can shrink the tumor considerably so it can be resected easily.
- Destroys maximum tumor cells in the target area.
- Tumor borders not visible to the naked eye can also be destroyed by radiotherapy.
- Improves quality of life by preventing resection of organs.
- Helps in palliative care by improving symptoms of cancer that is in the advanced stage.
- Its efficacy increases when used in combination with chemotherapy. It also increases the sensitivity of cancer cells.
- It is usually a painless procedure.
- No risk of bleeding and infection.
- It does not take much time only takes 10-15 minutes.
- Reduces recurrence of cancers of the breast, bowel, uterus, and prostate.
- In the anal region, radiotherapy prevents incontinence.
- Radiation therapy in clinics is a high-priced treatment. But it can be used to deliver radiotherapy sessions over a long period of time.
Side effects of radiotherapy and how to manage them?
As with any treatment option, there are side effects. It depends on the doses, frequency, and the part of the body exposed to radiation. The severity of the complication varies from patient to patient. Some patients continue their regular activities whereas some can’t do much activities due to fatigue. Some side effects may go away quickly. Others may take time as the healthy body tissues slowly recover from radiation damage.
Early side effects
Some side effects appear soon after radiation therapy is started. They are usually reversible and mild. They usually go away in a few weeks when the radiation therapy sessions are completed. These include fatigue, hair changes, skin changes, and mouth problems. The hair and skin changes are more pronounced near the target area.
Late side effects
Late side effects appear after months or years after receiving radiation therapy. They depend on the intensity and duration of radiation used in radiotherapy. They appear in normal tissues of the body that have received radiation. Therefore, cautious planning to be ensured before starting radiotherapy to avoid long-term side effects.
Common side effects
A feeling of exhaustion
One of the most common side effects of radiotherapy is feeling exhausted. Easy tiredness, low mood, and not able to perform normal work activities are similar presentations. This feeling of fatigue starts to appear after a few weeks of starting radiotherapy. Radiation destroys normal cells also, along with cancer cells. This mainly causes tiredness and increases in intensity with time. This feeling of fatigue does not improve with taking rest as compared to normal fatigue. It cannot be diagnosed by any laboratory testing. You have to describe it to the doctor, if it is not relieving with time and increasing in severity. It can be improved by:
- Going for a walk, doing yoga, maintaining fitness;
- Continuing your pre-radiation routine;
- Perform activities when you have more energy;
- Give sufficient time for rest;
- Read or listen to relaxing music;
- Seek help from family and friends;
- Write down how you feel daily so can keep track of it.
Skin changes
Radiation therapy damages skin cells which result in inflammation of the skin. It appears like sunburn because the skin becomes red, sensitive, and inflamed. The skin also becomes dry and scaly which causes itching. You should discuss this with your doctor so that they suggest you something for its treatment.
You can take care of your skin in the following ways:
- You should use clothing which is soft, loose and smooth.
- Do not scratch or rub your sensitive skin.
- As your skin is sensitive always use sunscreen before going out in the sun.
- Do not use hot or cold water use lukewarm water.
- An electric shaver can be used to remove hair from the treating area instead of blades, hair removal products, etc.
- You should always ask your doctor before using any powder, cream, lotion, perfume, deodorant, or oil on your skin.
- Adhesive bandages should not be applied to the skin.
- For radiotherapy of breasts, you should avoid using a bra.
Hair loss
Radiation therapy can result in hair loss only in the target area. If you are having radiotherapy of the prostate it cannot result in hair loss from the head. This hair loss is mostly reversible. The hair grows back when the treatment is finished. The hair may be thinner than before. You may shave the hair before the start of treatment.
You should avoid using hair dryers, hair spray, and hair dye. Wash your hair with baby shampoo and use a soft towel. Cover your head with a hat or turban when you go out in the sun.
Loss of appetite
With radiotherapy, you need to take extra calories. The body requires energy to heal normal cells damaged by radiation. But you may experience loss of appetite. Here are some tips to maintain your appetite:
- Preparing high calorie and protein diet is very essential for muscular growth.
- Ask the advice of your doctor before trying any nutritional supplements.
- Eat small meals at least five to six times.
- Drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration.
- You can eat with friends and family this will motivate you to eat.
Mouth changes
Radiation therapy in the head and neck region can cause a number of mouth problems. These include:
- Oral ulcers;
- Dryness of mouth;
- Dental caries;
- Stiffness of the jaw;
- The thickness of saliva;
- Bad breath;
- Infection of the gums.
You should share these problems with your doctor for its treatment. These problems can be avoided in the following ways:
- Dryness of the mouth can be avoided by drinking plenty of water and fluids;
- The mouth should be cleaned daily with an extra soft toothbrush two times a day;
- If you notice any dental problem show it to a dentist timely;
- Do the daily exercise of your jaw by opening and closing;
- Toothpaste containing fluoride should be used.
Diarrhea
Diarrhea occurs in radiation therapy of the Pelvic region. Discuss this with your healthcare provider for its treatment. Following diet changes can help:
- A liquid, soft diet should be taken;
- Low fiber diet should be used;
- Frequent small meals should be taken;
- Milk and dairy products should be avoided.
Sex and infertility issues
Pelvic region radiotherapy can cause sex issues in both males and females in the following ways:
- Decrease libido in both men and women;
- Dryness in the vagina which can be treated by using lubricants;
- Erectile dysfunction;
- Painful ejaculation;
- It can cause menopause in women and decreased sperm count in men.
These can improve back to normal once treatment is completed.
Lymphoedema
It can damage lymph vessels in the body which causes swelling in the body which is painful. It occurs most commonly in the arms and legs. This can be prevented by regular exercise.
Conclusion
Radiation therapy in clinics worldwide has markedly improved the morbidity of cancer patients. With advancements, radiation therapy is continuously growing to improve precision and accuracy. The technological resources continue to advance on an international level. Radiation therapy is positioned to play a critical role in comprehensive cancer care.